API Testing
By Srinesh Nisala
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/srinesh-nisala/
- GitHub: https://github.com/s1n7ax
Pre-requisites
[!NOTE] It's important to understand the basics of HTTP and RESTful than how to use a specific tool.
Website vs Web Service
- Website: Deliver human-consumable content via a browser
- Interaction is user-driven (clicks, scrolls, inputs)
- Technologies: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Web Service: Enable machine-to-machine communication over the web
- Data is transferred in structured formats (e.g., JSON/XML)
- Technologies: REST, SOAP, GraphQL
Exercise 1: HTTP Request and Response
- Open a new browser tab
- Open the network tab in the developer tools
- Visit a website (e.g., https://www.google.com)
- Observe the first network requests made by the browser
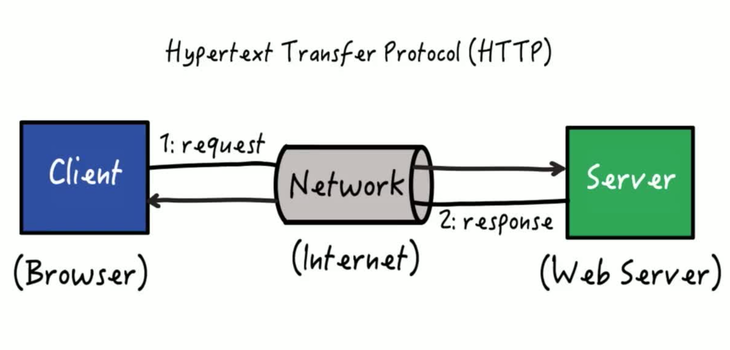
Exercise 2: Calling a web service using HTTP
- What is json placeholder?
- Open network tab in the developer tools
- Go to https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts
- Observe the
- Response Data
- Response Status Code (
ctrl+shift+rif you are getting 304)
Exercise 3: Using other tools to call a web service
- Open network tab in the developer tools
- Go to https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1
- Observe the response data
- Use
xhto make the same requestxh https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1 - Use Bruno to make the same request
- Create a new collection
- Create a new request
- Set the method to
GET - Set the URL to
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1 - Click on
Send
Exercise 4: Using Bruno to make a POST request
- Create a new request
- Set the method to
POST - Set the URL to
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts - In the body tab, select
JSONand enter the following JSON data:
{
"title": "foo",
"body": "bar",
"userId": 1
}
- Click on
Send
Exercise 5: Using REST Assured to make a GET/POST request
- Open https://github.com/s1n7ax/lecture-api-testing in codespace
- Send a request to
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1and get post - Add validations to check if the response status code is
200 OK - Add validations to check if the response body contains the correct title
- Send a POST request to
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/postsand create a new post - Add validations to check if the response status code is
201 Created - Add validations to check if the response body contains the correct title and body
HTTP vs RESTful
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol, 1996): source
- Protocol for transferring data over the web
- RESTful (Representational State Transfer, 2000): source
- An architectural style (not a protocol!) for designing networked applications
HTTP Methods
- GET: Retrieve data from the server
- POST: Send data to the server to create a new resource
- PUT: Update an existing resource on the server
- DELETE: Remove a resource from the server
- PATCH: Partially update an existing resource on the server
- OPTIONS: Retrieve the allowed HTTP methods for a resource
HTTP Request/Response Data
- Request: Client sends a request to the server
- Method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
- Headers (Metadata about the request)
- Body (Data sent with the request, optional)
- Response: Server sends a response back to the client
- Status Code (Indicates the result of the request)
- Headers (Metadata about the response)
- Body (Data returned by the server, optional)
HTTP Status Codes
- 1xx: Informational
- 2xx: Success
- 200 OK: Request succeeded
- 201 Created: Resource created successfully
- 204 No Content: Request succeeded, no content to return
- 3xx: Redirection
- 301 Moved Permanently: Resource moved to a new URL
- 302 Found: Resource temporarily moved
- 4xx: Client Error
- 400 Bad Request: Invalid request syntax
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication required
- 404 Not Found: Resource not found
- 5xx: Server Error
- 500 Internal Server Error: Generic server error
- 502 Bad Gateway: Invalid response from upstream server
- 503 Service Unavailable: Service temporarily unavailable
- 504 Gateway Timeout: Upstream server did not respond in time